What is FDM 3D printing?
Table of Contents
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is an additive manufacturing process that belongs to the material extrusion family. In FDM, an object is built by selectively depositing melted material in a predetermined path layer-by-layer. The materials used are thermoplastic polymers and come in a filament form.
FDM 3D printing is the most widely used 3D Printing technology: it represents the largest installed base of 3D printers globally and is often the first technology people are exposed to. In this article, the basic principles and the key aspects of the technology are presented. A designer should keep in mind the capabilities and limitations of the technology when fabricating a part with FDM, as this will help him achieve the best result.
How does FDM 3D printing work?
The FDM fabrication process:
- A spool of thermoplastic filament is first loaded into the printer. Once the nozzle has reached the desired temperature, the filament is fed to the extrusion head and in the nozzle where it melts.
- The extrusion head is attached to a 3-axis system that allows it to move in the X, Y and Z directions. The melted material is extruded in thin strands and is deposited layer-by-layer in predetermined locations, where it cools and solidifies. Sometimes the cooling of the material is accelerated through the use of cooling fans attached to the extrusion head.
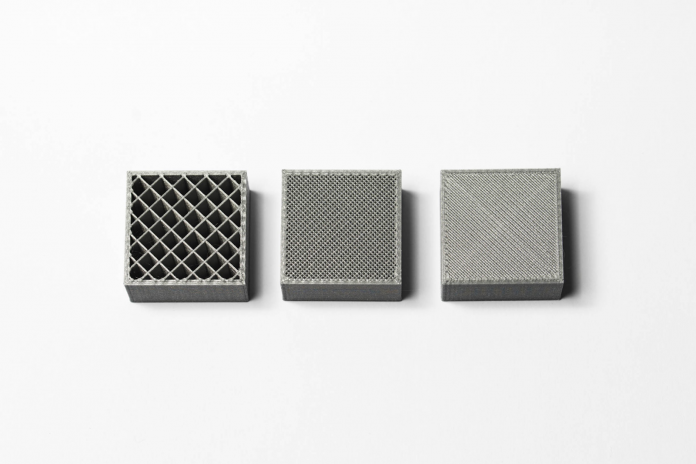
III. To fill an area, multiple passes are required (similar to coloring a rectangle with a marker). When a layer is finished, the build platform moves down (or in other machine setups, the extrusion head moves up) and a new layer is deposited. This process is repeated until the part is complete.
Adjust basic settings with FDM 3D printing
Another video you can find on YouTube covers the basics you have to use to create stronger FDM 3D prints. There are several slice settings to change the strength of a product that is going to be FDM 3D printed, including the fill percentage, the surface thickness, the layer height, and the width of the extrusion for example. But one configuration that is often overlooked is the so-called infill overlap, which affects the degree of integration between the perimeters and the infill. Usually only a small increase is required to make the print a lot stronger. It is definitely advised to at least once try this tip to examine if it actually made your created product a bit stronger, which will also be the case when using the other tips.
Benefits of FDM 3D printing in 2021
The key advantages of FDM 3D printing are summarised below:
- FDM is the most cost-effective way of producing custom thermoplastic parts and prototypes as an online machine shop.
- The lead times of FDM are short (as fast as next-day-delivery), due to the high availability of the technology.
- A wide range of thermoplastic materials is available, suitable for both prototyping and some non-commercial functional applications.
Rules of Thumb to learn
- FDM can produce prototypes and functional parts fast and at a low cost from a wide range of thermoplastic materials.
- The typical build size of a desktop FDM 3D printer is 200 x 200 x 200 mm. Industrial machines have a larger build size.
- To prevent warping avoid large flat areas and add fillets in sharp corners.
- FDM is inherently anisotropic, so it is not recommended for mechanically critical components.